Objects/classes
Notes Procedures denoted in boldface, as separate sections.
n-D does not include time
ref. [4] in exc.bib
Base classes
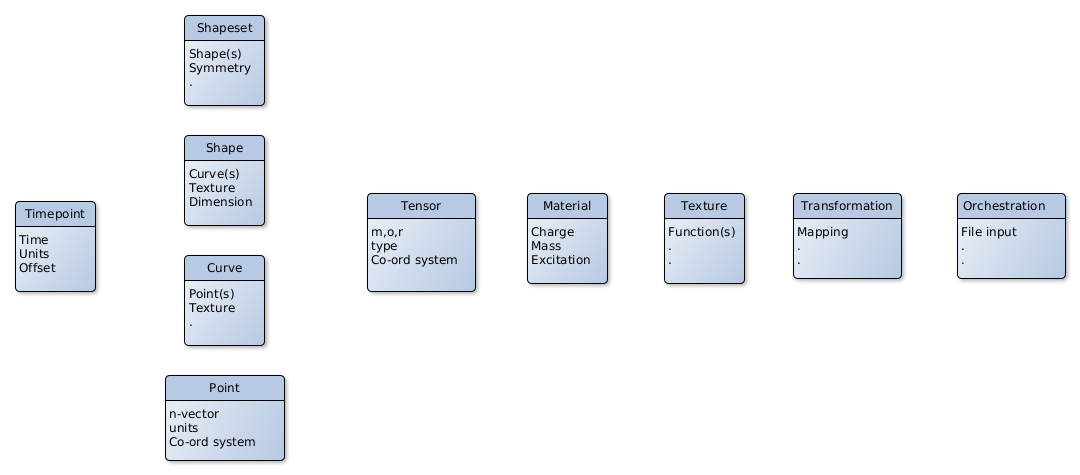
The proposed base classes for NEPTUNE are listed below and shown graphically in Figure 6.1.
-
• Timepoint : point in physical time Attributes of time, units, offset (Alternatively just real scalar)
-
• Point : point in n-D space
many make curve, shape;
is particle location in n-D ; Attributes of n-vector, units, coordinate system (Alternatively just real n-vector) -
• Curve : parts are one or more points, straight lines or textures or from CAD input or CSG input;
many make shape;
is shape boundary, is particle trajectory, is ray -
• Shape : parts are curves and textures, planar rectangles, or surfaces from CAD input or CSG input;
many make Shapeset;
is surface which aggregates as BC -
• Shapeset : parts are shapes, regular lattice, or volumes from CAD input or CSG input;
is finite element geometry, is unstructured mesh, is surface geometry of body, is volume in n-D, \(n\geq 3\) ;
helps defines field
Attributes of degree of toroidal symmetry -
• Tensor : parts are \(m\) numbers at a point, order \(o\), type eg. udd, and density \(r\) in n-D coordinate system of type c;
is (\(m=3\), \(o=1\), \(n=3\)) velocity, is (\(m=1\), \(o=3\), \(n=3\)) density,
is (\(m=1\), \(o=0\), \(n=3\)) temperature, is (\(m=3\), \(o=0\), \(n=0\)) is array;
many help make field (u denotes contravariant, d denotes covariant, c defines cartesian, cylindrical, toroidal coordinates, \(r=0\) usually) -
• Material : from database input ;
helps make body, particle, many make matexture, plasma
Attributes of charge, excitation level and mass -
• Texture : parts are mathematical library functions, particularly mathematical library interpolation functions - see Section 6.3
aggregates as matexture, BC -
• Transformation : mathematical formula defining geometry transformations on point and tensor (co- and contra-variant) \(\bf {\bar {x}}\rightarrow \bf {x}\)
-
• Orchestration : parts are from configuration file input see Orchestration, model, framework
Aggregates
-
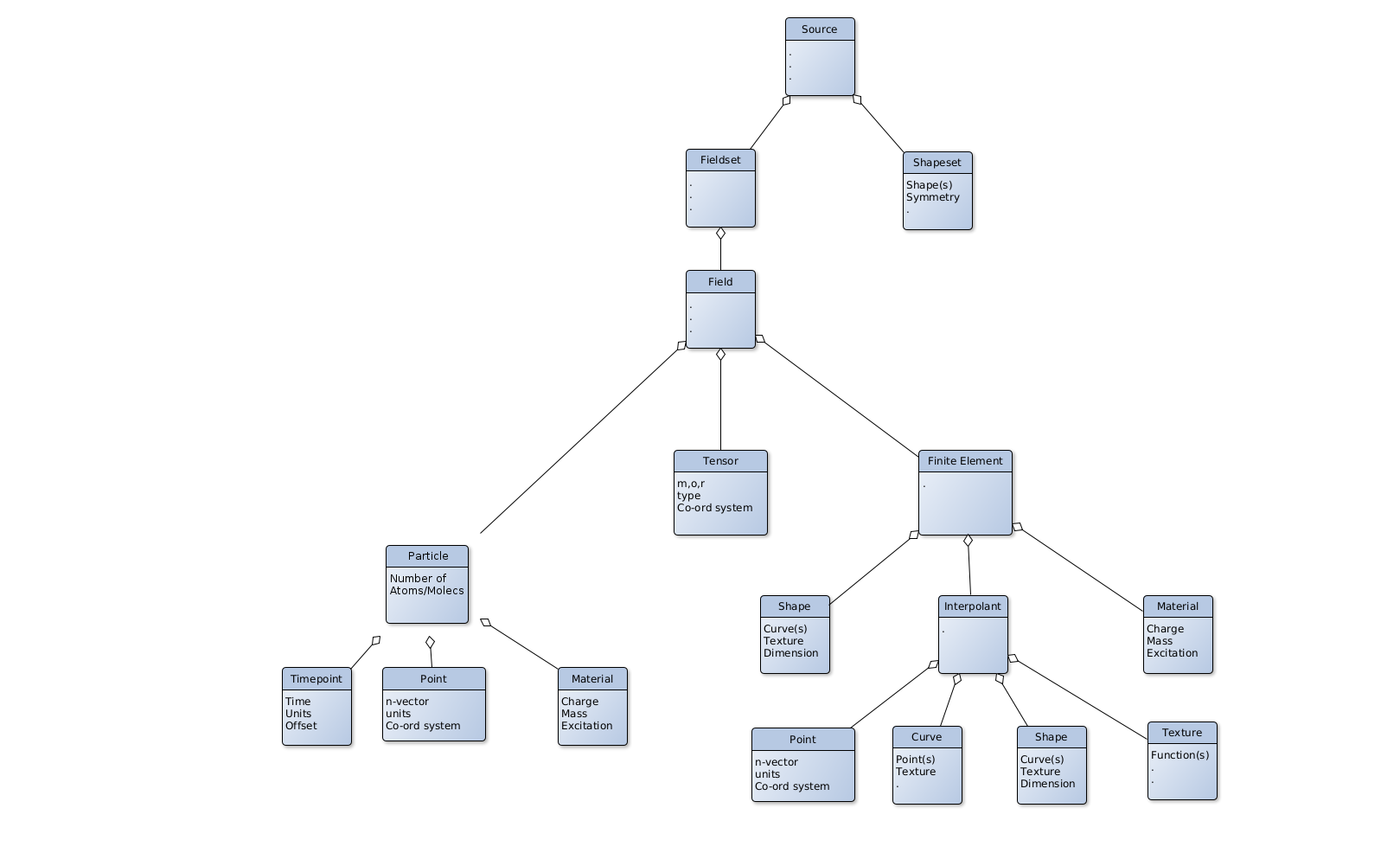
• Particle : parts are location, velocity, material;
Attributes of particle weight -
• Interpolant : parts are points, curves, shapes, textures, or timepoints, textures
-
• Diagnostic : parts are DSL input instructions Diagnostic Processing, fieldset
-
• FE (Finite element) : parts are shape, interpolant, material
-
• Field : parts are tensors and finite elements, or particles;
many make fieldset -
• Fieldset : parts are fields
-
• DE (Differential equation) : parts are operators (DSL input), IC, BC and source
-
• Model : parts are Solution of DEs
-
• Source : parts are shapeset, fieldset. See Figure 6.2.
-
• Matexture : parts are materials, textures
-
• Body : parts are shapeset, matexture
-
• BC (Boundary Condition) : parts are surface, material, texture
-
• GEOQ (Geometry plus B-Equil) : parts are shapeset, field
Simple inherits
-
• HDS (Hierarchical Data Structure) : multi-octree, is a shapeset
-
• Trajectory : particle position as time varies, is a curve
-
• IC (Initial Condition) : is a fieldset
Solution of Differential Equations
Use in part ABSTRACT CALCULUS and PUPPETEER patterns (cf. GoF FACADE) from Rouson et al. ref. [98], see Section 6.4.
Diagnostic Processing
-
1. Read configuration file
-
2. Determine whether any diagnostic needed at present physical time
-
3. Select input fieldset
-
4. Select diagnostic type, use in part ABSTRACT CALCULUS from Rouson et al. ref. [98]
-
• Initial logs
-
– UUID
-
– Key input data
-
– Key properties, eg. LCFS
-
-
• Combinations of
-
– Field / quadratic field (eg. power, flux quantity) / general formula
-
– Point, line integral, surface integral, volume integral
-
-
• Mass/charge, momentum/current and power balances
-
• Turbulence statistics - cross-correlations, spectra (not particle, ray)
-
• Difference between solutions/experiment (RMS as ‘skill’) (not particle, ray)
-
• See “emergent physics as diagnostic” in imas_objects.tex
-
-
5. Calculate output fieldset
-
6. Set output format
-
7. Output fieldset to disk, screen
Orchestration
-
1. UQ Framework VECMAtk and FabNEPTUNE
-
2. GUI
-
3. CLI
-
4. Possible restart (OLYMPUS logic, Fig.1 of ref. [60])
-
5. Initialise from functions.md
-
6. Solution from functions.md